AMRAAM Missile Deal Approval — Allied Airpower Ramps Up
The AMRAAM missile deal approval wave is reshaping allied airpower from Europe to the Indo-Pacific. Multiple DSCA notifications in September 2025—most notably Germany’s request for up to 400 AIM-120D-3s (~$1.23B)—underline a coordinated uplift of beyond-visual-range (BVR) capability across F-35, F-15, F-16, Typhoon and NASAMS operators. dsca.mil+2 dsca.mil+2
Note on the headline claim: several outlets reported a “$41.6 billion, 30-nation approval”. Authoritative U.S. government sources (DSCA) have not published a single package at that value. Some reports appear to conflate a $41.6 million contract modification (to a ~$2.51 billion umbrella) with a multibillion program total. We therefore treat the global $41.6 billion figure as unconfirmed at this time.
Why does it matter now?
The AMRAAM missile deal approval sequence lands as China fields PL-15/PL-16 and Russia employs R-37M at range. Allied air forces need credible first-shot reach, robust data links, and a strong ECCM to survive in contested skies. Germany’s D-3 case signals how F-35 users will standardise around a common BVR baseline, with logistics and training benefits across NATO. dsca.mil+1
Moreover, the AMRAAM missile deal approval aligns with a steady industrial ramp. RTX says F3R (Form, Fit, Function Refresh) upgrades are in production, and the missile just achieved its longest-known shot in USAF testing—demonstrating extended time-of-flight performance for fifth-gen fighters. RTX+1
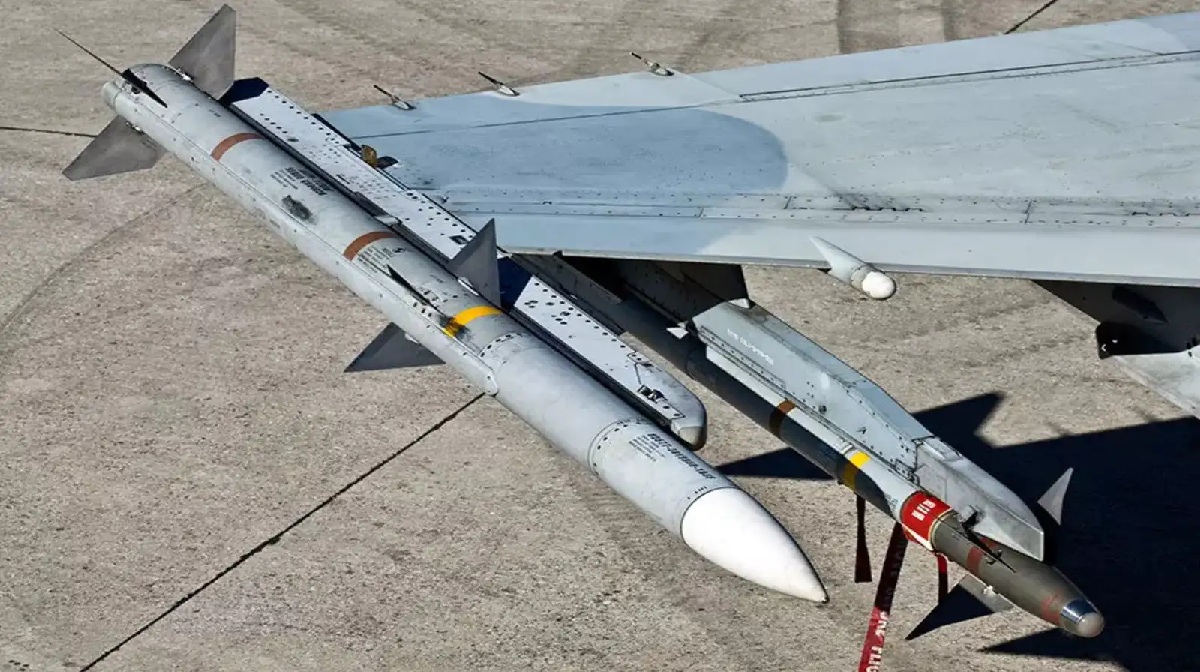

What’s actually approved?
The AMRAAM missile deal approval that is fully on record includes:
Germany – AIM-120D-3 (up to 400) for an estimated $1.23B (DSCA notification, 25 Sept 2025). This supports Germany’s F35A program and NATO integration. dsca.mil+2 dsca.mil+2
The approval process for the AMRAAM missile deal is happening at the same time as a separate $3.5 billion agreement to produce more AMRAAM missiles for the U.S. and its allies this summer, which will help restock their supplies and provide for 19 partner countries—showing that there is Business Insider
Finally, media reports suggest Pakistan’s inclusion among foreign buyers in broader contracting actions; however, the amounts, quantities, and timelines for Islamabad remain unclear in official notices. Treat these claims with caution until DSCA publishes a country-specific case. This process keeps the AMRAAM missile deal approval discussion grounded in verifiable filings. The Economic Times + 1
Capability snapshot: C-8 VS D-3
The AMRAAM missile deal approval spans two top-line configurations:
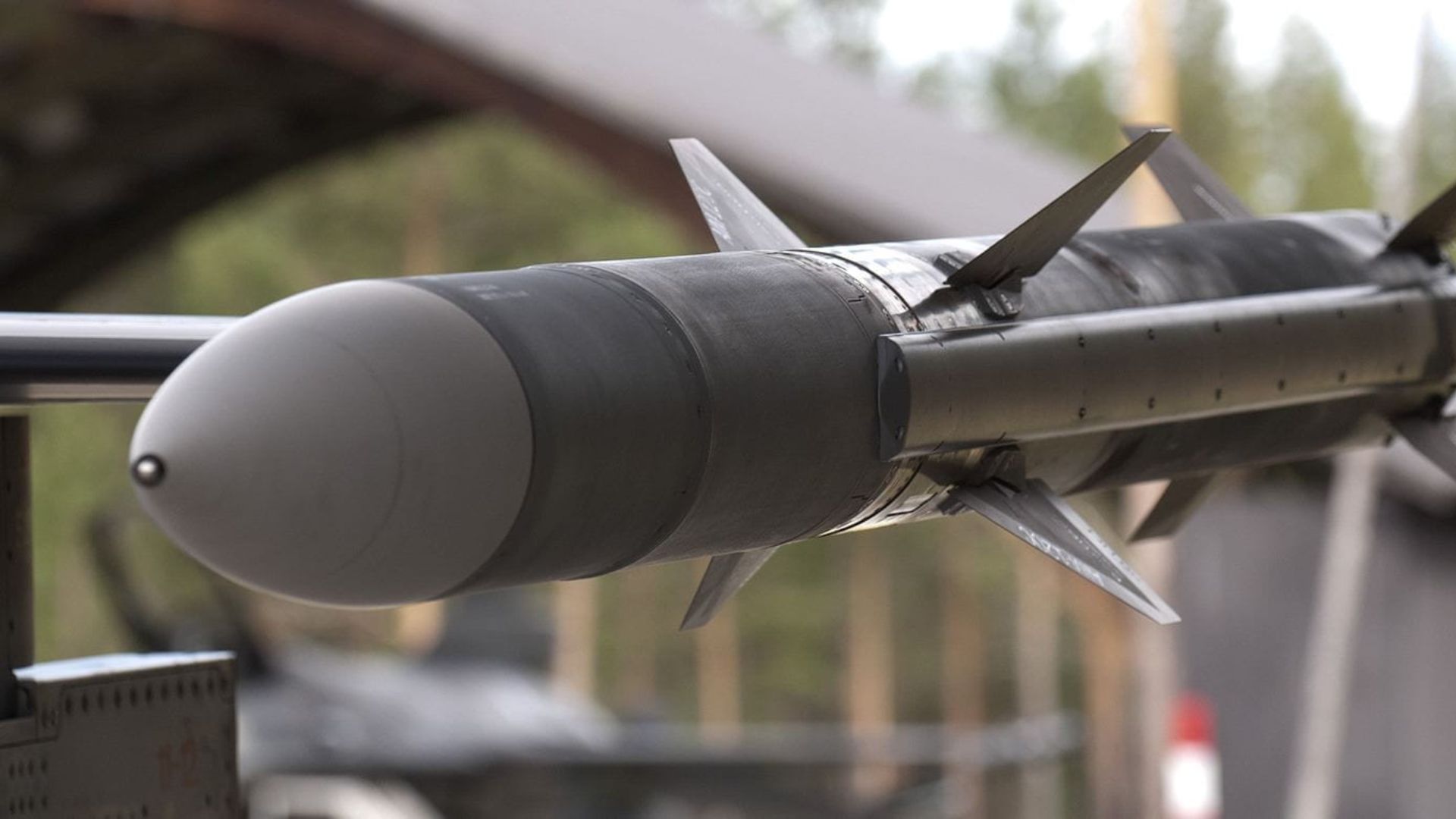
- AIM-120C-8: export-focused, improved ECCM, refined guidance logic; widely integrated across F-16, F/A-18, Gripen, Typhoon and selected F-35 users.
- AIM-120D-3: two-way datalink, GPS-aided navigation, and refreshed electronics via F3R; designed for high-G, manoeuvring targets, and long-range shots from F-22/F-35.
| Feature | AIM-120C-8 (Export Variant) | AIM-120D-3 (Advanced Variant) |
| Range | Up to 100 km+ | Up to 160 km |
| Guidance | Active radar, inertial/GPS mid-course updates | Enhanced active radar, GPS, two-way link |
| Speed | Mach 4 | Mach 4+ |
| Warhead | High-explosive fragmentation | High-explosive fragmentation |
| Platforms | F-16, F/A-18, Typhoon, Gripen | F-22, F-35, NASAMS |
| Key Upgrade | ECM resistance, improved processors | Anti-jam software, F3R electronics |
F3R is the backbone of the AMRAAM missile deal approval story—updated circuit cards and software keep the missile relevant against modern jamming and low-observable targets. RTX confirms the F3R D-3 is in production and recently enabled the longest known AMRAAM shot during USAF trials. Air & Space Forces Magazine + 3PR Newswire + 3RTX + 3
Interoperability: NASAMS and cross-domain utility
One major benefit of approving the AMRAAM missile deal is cross-domain standardisation. AMRAAM doubles as the baseline interceptor for NASAMS, giving air forces a common missile across fighters and ground-based air defences.
That simplifies training, spares, and mission data across allied networks. The coming AMRAAM-ER variant further stretches NASAMS’ envelope with larger rocket motors. kongsberg.com+2RTX+2
This integration idea backs up the approval story for the AMRAAM missile deal: using one type of seeker, connected data links, and shared logistics—allowing groups to quickly set
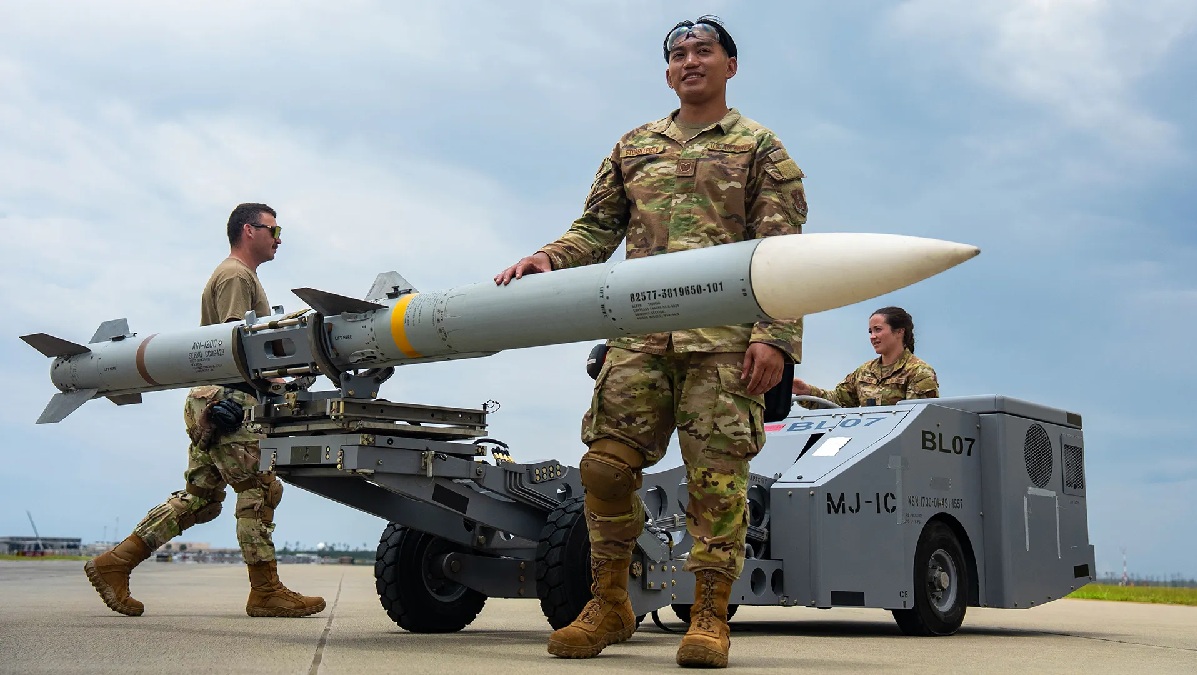

Industrial outlook: production and sustainment
The approval of the AMRAAM missile deal is based on a real industrial ramp. Recent corporate guidance and reporting indicate higher output year-over-year, with ~50–60% growth over 2024 levels and continued investment in production tooling and electronics refresh. That lends credibility to accelerated deliveries through the decade, a key plank for allies rebuilding inventories. investors.rtx.com+1
However, the approval of the AMRAAM missile deal still faces constraints, as solid-propellant supply, seeker components, and microelectronics continue to be critical issues within the missile industry. The difference now is volume commitment and a stable, multi-year order book, which helps suppliers scale.
Geopolitics: shaping the BVR balance
Strategically, the AMRAAM missile deal approval consolidates a Western BVR baseline while adversaries push longer-reach options. Standardisation offers practical gains—shared tactics, mission-data alignment and joint training. It also creates policy leverage: software keys, encryption, IFF modes, and data links bind recipients to Western networks, improving coalition cohesion.
For NATO, the AMRAAM missile deal approval complements F-35 expansion and strengthens the deterrence layer on the eastern flank. Distributing advanced BVR capability among partners to prevent any one stockpile from becoming a bottleneck is in line with integrated deterrence for the Indo-Pacific.
Tech horizon: JATM and AMRAAM-ER
Even with the AMRAAM missile deal approval, the U.S. is fielding the AIM-260 JATM as a tier-above capability. Expect a mixed inventory: JATM at the top end, AMRAAM as the allied workhorse, and AMRAAM-ER extending ground-based coverage.
This layered approach protects coalition flexibility while preserving the cost-effective, widely integrated AMRAAM backbone. The AMRAAM missile deal approval therefore complements—not competes with—next-gen missiles. kongsberg.com+1
References
- DSCA: Germany – AIM-120D-3 approval summary (Sep. 25, 2025). dsca.mil
- Business Insider: $3.5B AMRAAM award to RTX for the U.S. and 19 allies (August 2025). Business Insider
- RTX: “Longest known AMRAAM shot” & F3R update (Sep 16, 2025). RTX
- Kongsberg: NASAMS employs AMRAAM/AMRAAM-ER (product page). kongsberg.com